The majority of organic traffic (bots or hackers) to e-retail sites has malicious intent. This article will take you through the most important eCommerce security risks and threats that are currently plaguing e-retail. Here are some eye-opening statistics and figures from 2022:
Over 91% of eCommerce businesses reported at least one cyber incident last year.
Almost 98% of all cyber-attacks in e-retail have financial motives.Online payment fraud caused $41 billion in losses globally in 2022.Around 22.6% of all login attempts on e-retail websites were account takeover attempts. Here are a few eye-opening stats and figures from 2022:
Over 91% of eCommerce businesses reported at least one cyber incident last year.
Almost 98% of all cyber-attacks in e-retail have financial motives.
Online payment fraud caused $41 billion in losses globally in 2022.
- Around 22.6% of all login attempts on e-retail websites in 2022 were account takeover attempts.
- Let’s examine the most significant eCommerce security threats you must consider when planning your platform’s defenses.
- Financial Fraud
- Criminals rely on various fraud strategies to steal money from E-comm shoppers and websites. These are the most common:
Payment Card Fraud:

Since every eCommerce website accepts online payments, these pages become a prime target for payment card scams. Criminals often use stolen or counterfeit credit card info for unauthorized transactions, leading to financial losses for cardholders and the business.
Account takeovers:
A takeover occurs when an attacker gains unauthorized access to a customer account on your eCommerce website. Once an intruder takes over the account, the threat actor makes fraudulent purchases or exploits stored payment data.Chargeback fraud:
Chargeback fraud (or friendly fraud) happens when a “customer” makes a purchase, receives the product, and fraudulently attempts to get a refund using the chargeback process from the issuing bank. Most eCommerce businesses accept gift cards and vouchers for payment. Fraudsters also often use stolen credit cards to purchase gift cards and then resell them to unsuspecting customers.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering is an umbrella term for various forms of manipulation that enable a threat actor to deceive victims and get them to either: Share sensitive info (e.g., login credentials or credit card details).
Perform security-compromising actions (e.g., click on a file that installs malware).
Criminals using social engineering to target eCommerce customers usually rely on a combination of the following tactics:
Phishing:
- Phishing occurs when an attacker sends deceptive emails or messages to customers, posing as a legitimate business or institution. Threat actors use phishing to trick targets into revealing passwords or credit card details, after which criminals log into the account and start shopping.
- Pretexting:
This strategy involves creating a false pretext or scenario to trick the target into disclosing info. For instance, an attacker might pose as somebody from your customer support team and request a customer to share account details.
- Baiting: This social engineering tactic uses the promise of an award (such as a giveaway or discount) to entice the victim. For example, a criminal may send one of your customers a fake giveaway award and instruct the victim to log in on a fake duplicate website that steals login credentials.
- Click HijackingClick hijacking (also known as
- clickjacking or
UI redressing
) enables an attacker to overlay or hide elements on a page to trick a user into clicking on a malicious element.Clickjacking enables a criminal to trick customers into clicking buttons or links that perform unintended actions, such as:Change account settings.Add a product to the cart.Execute a fraudulent transaction.
For example, a hacker might compromise your E-comm website and set a hidden element on top or underneath the “PLAY” button on your home page’s video. A criminal who has access to the database that stores sensitive information can perform a fraudulent transaction by tricking a user into clicking on the button. In the case of eCommerce websites, a breach typically involves a threat actor gaining access to one of two data types:
- Personally identifiable information (PII) of customers, such as names, addresses, emails, or phone numbers.
- Financial data, such as credit card numbers or bank account details.
- Data breaches are among the most significant eCommerce security threats. An intruder gaining access to or stealing sensitive data has massive consequences, such as:
A threat actor using PII to commit identity theft or financial fraud.
Massive monetary losses for the business (costs of investigating the breach, mitigating damages, notifying customers, improving cybersecurity measures to prevent similar attacks in the future, etc. ).
Substantial reputational hits that damage customer confidence and negatively impact future sales.
- Regulatory fines for failing to protect customer data.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack enables a threat actor to intercept and potentially alter the communication between two parties without their knowledge or consent. Here’s how a MitM attack can impact an eCommerce website:
- Data interception:
- An attacker intercepts sensitive data exchanged between customers and the website. The criminal gets to steal login credentials, payment card details, and personal info, which enables unauthorized access to accounts and identity theft.
- Transaction tampering:
- Some MitM attacks modify the contents of communications. A threat actor alters transaction details or payment amounts, causing financial losses for the customer and the E-comm business.
Malware setup:
Criminals often use MitM attacks as a vector for delivering malware to unsuspecting customers. Threat actors inject malicious code into web traffic and try to infect the customer’s device with malware.
- Most MitM attacks occur when customers use a vulnerable Wi-Fi to shop on e-retail websites.Malware Infections
- Malware (short for malicious software) is an umbrella term for any software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to a system. Here are the types of malware that pose the most danger to eCommerce websites:Credit card skimmers:
- Skimmers target E-comm platforms to steal payment card info from customers. This type of malware usually infects a website’s checkout or payment process. A skimmer captures data from payment forms and relays info to the hacker.Backdoors, remote access trojans (RATs), and rootkits:
These types of malware allow unauthorized access to a compromised website. Once inside, intruders gain control over the website and steal data, modify content, or set up more dangerous forms of malware.
Keyloggers:
This type of malware records keystrokes made by users. If a customer falls victim to a keylogger, the program will capture credentials and send the login info to the attacker.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a considerable threat in all industries, and eCommerce is no exception. This malware type encrypts files, after which the attacker demands payment to send a decryption key.
- Malicious Code InjectionsCode injections enable an attacker to inject malicious code into a website’s page or script. Criminals most commonly inject code via a vulnerability within the CMS or through a third-party plug-in.
- Here is a list of the code injections which pose the greatest risk to eCommerce websites:SQL Injections:
- These attack inject malicious code in a database query allowing the hacker manipulate or extract files. SQL injections can affect any web application or website that uses an SQL database, such as MySQL, Oracle Sybase Access Ingres etc. Cross-site scripting attacks (XSS): These attacks inject malicious scripts into web pages (most often in the form a browser side script) to compromise visitors. As a result, the attacker gets to steal session cookies, gain unauthorized access to user accounts, or redirect traffic to malware-infected websites.
Remote Code Execution (RCE) injections:
RCE injections enable criminals to execute arbitrary code on the server hosting the eCommerce website. In most cases, RCE is a way to gain complete control of the server.
XML External Entity (XXE) injections:
- These injections exploit flaws in XML parsers and processors, tricking the parser to disclose sensitive data or perform unintended actions (e.g., access local files or execute a remote request).More skilled criminals also use malicious code injections as a delivery mechanism for malware.
- DoS and DDoS AttacksDenial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks enable a threat actor to overwhelm a website with an excessive volume of traffic or requests. These attacks are carried out by hackers using botnets, which are networks of malware-infected computers. Downtime directly translates to a loss of revenue as customers cannot access the website and make purchases.
- Prolonged and frequent disruptions damage the reputation of an eCommerce website. Over time, customers lose their trust and begin to use other service providers. Also, frustrated users tend to share negative experiences online, which further harms the website’s reputation.Read our DDoS prevention guide to learn how to stop criminals from disrupting your operations. If you’d like professional help in minimizing the risk of DDoS attacks, check out our DDoS protection page.
- Malicious BotsWhile there are legitimate bots (such as search engine crawlers), there are also malicious bots that cause harm to websites. Here’s what risks bots present to an eCommerce website:
Malicious bots often target e-retail websites to carry out account takeover attacks. The bot uses automated methods to try and gain unauthorized access to accounts.
Some threat actors use bots for inventory scalping. Scalping is the automatic purchase of high-demand products to reduce stock and prevent customers from purchasing them. This information helps to undercut pricing strategies. That info helps with undercutting pricing strategies.
Bot “armies” of malware-infected devices are the go-to method for performing DDoS attacks that overwhelm the website’s resources.
Some bots scrape product info, images, or other content from eCommerce websites. Later, the person collecting data can create counterfeit products or set up a fraudulent website.
Some more sly competitors also use bots to click on paid ads that drive traffic to the site and drain budgets from online retailers.
Weak Authentication and Authorization
Poor authentication (the process of verifying the identity of users) and authorization (determining the privileges of authenticated users) mechanisms are major eCommerce security threats. The most common examples of weak practices are easy-to-crack passwords or a lack of two-factor authentication.
When these mechanisms are weak, the business risks various security incidents, including:
- Account compromises that result in financial fraud, data theft, or misuse of PII.
- Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Intruders being able to perform actions they shouldn’t have permission for (e.g., access to admin functions and backend systems).
- Privilege escalations that enable a threat actor to elevate privileges and gain access to more critical systems or data within the infrastructure.
- Weak authentication and authorization practices also often cause non-compliance with industry regulations (such as PCI or GDPR), which often leads to legal consequences.
Brute Force Attacks
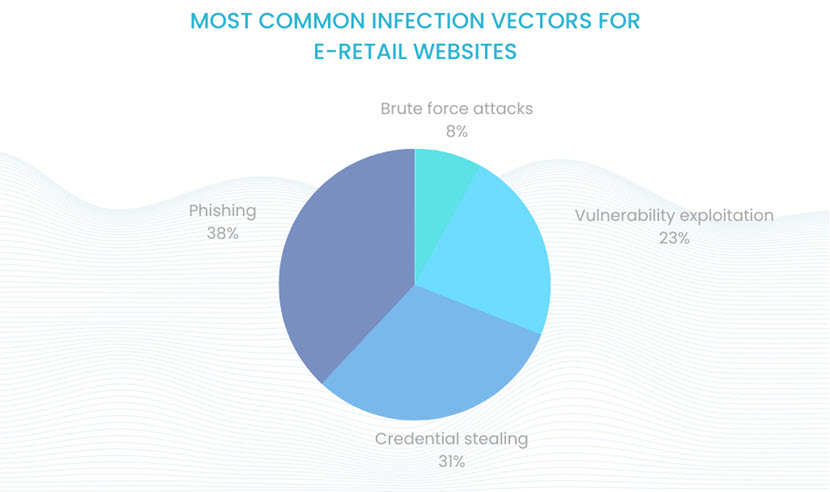
In a brute force attack, a threat actor uses a bot to systematically try different combinations of usernames and passwords in an attempt to guess the correct credentials.
The easier the password is, the faster a bot guesses it and gains access. For example,
an average bot can “crack” a 7-character password with letters, numbers, and symbols in around 31 seconds
- .
- Here’s why brute force attacks are a major concern for eCommerce websites:
- Successful brute force attacks grant unauthorized access to customer accounts, which enables an attacker to make unauthorized purchases. Account takeovers also often lead to the misuse of personal info.
- In some cases, brute forcing enables a threat actor to hack into admin portals or backend systems.
Brute forcing is also prone to resource consumption if you do not take proper precautions. Such a scenario often degrades website performance, increases server load, and leads to downtime.
eCommerce Security Solutions
Below is an overview of the most effective security measures that keep eCommerce platforms safe from unauthorized access, data breaches, fraud, and other malicious activities discussed above.
Secure Payment ProcessingSecure payment processing protects customer payment info during online transactions. This precaution is vital to eCommerce security as it enables you to:Protect sensitive data.
Maintain customer trust.
- Comply with industry regulations.
- Most eCommerce websites use third-party payment gateways to handle online transactions. Gateways are intermediaries that act between the website, financial institutions and customers. Secure payment processing solutions that offer the following features will keep the gateway secure.
Data in transit encryption that ensures all payment data remains safe during transmission. - Tokenization that replaces sensitive payment card data with unique identification tokens to reduce the risk of storing sensitive card data on your servers.
Address Verification Service (AVS) that verifies whether the billing address matches the one associated with the credit card.
Conduct regular vulnerability assessments of the payment processing system to identify flaws and ensure compliance with security standards.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is an encryption protocol that protects the communication between a web server and a user’s browser. SSL protects transmitted data from interception and tampering. To implement SSL encryption you will need an SSL Certificate issued by a trustworthy certification authority (CA). There are various types of SSL certificates available, including:
- Domain Validation (DV) certificates.
- Organization Validation (OV) certificates.
- Extended Validation (EV) certificates.
Remember to keep SSL certificates up to date and configure your web server to enforce HTTPS (HTTP over SSL/TLS) connections (represented by a green lock sign that says “secured” next to the URL bar). HTTPS will also boost your eCommerce website’s rankings on Google.
- Strong Password Enforcement
- Weak passwords make customer accounts vulnerable to brute-force attacks and unauthorized access attempts. Promote strong password practices to enhance eCommerce security and protect user accounts.
- Consider implementing the following measures:
Set minimum requirements for customer passwords (e.g., minimum length, a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, mandatory use of special characters, etc.). Apply the same principle to your admins and employees.
Implement checks during password creation to ensure users meet the required complexity criteria.
Use a password expiration policy to ensure users change their credentials periodically.
Remember to
- find a balance between password security and user experience
- . Remember to
- find a balance between password security and user experience
. ).
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires a customer to provide two or more pieces of evidence to verify their identity. That way, you make it more difficult for an attacker to gain unauthorized access even if they obtain someone’s username and password (e.g., through a phishing attack or a data breach).
Here’s how MFA typically works:
- The user types in their username and password to log in to their account.
- Once the website verifies credentials, the platform prompts the user for a second form of authentication.
- The second factor in the MFA process can be one of the following:
One-time password (OTP) tokens the user receives through a text message, email, or mobile app.Biometric factors such as fingerprint or facial scanning.Hardware tokens.
Security questions.
Push notifications on the registered mobile device.
MFA adds a valuable extra layer of security, as the attacker requires physical access to the user’s mobile device or knowledge of the second authentication factor to breach an account.
- Fraud Detection Tools
- Fraud detection tools rely on various techniques to identify and mitigate fraudulent activity on your eCommerce platform. These programs use machine learning algorithms and behavioral analysis to detect anomalies associated with fraudulent activities.
Your fraud detection system should continuously monitor transactions in real-time and examine various attributes, such as:
- Transaction amounts.
- Transaction frequency.
- Customer location.
- User behavior.
- Unusual transactions trigger an alert or additional verification steps. The fraud detection system tracks the unique characteristics of devices, such as IP addresses, browser settings, device identifiers and more. to detect suspicious patterns or device anomalies.
Anti-Malware and Anti-Virus Software

Anti-malware and anti-virus tools protect the underlying infrastructure of your eCommerce website and end-user devices accessing the platform. These programs help prevent various cyber threats capable of infecting servers and compromising customer data, including:
- Viruses.
- Worms.
- Trojans.
- Ransomware.
- Spyware.
- Adware.
- Keyloggers.
Fileless malware.
These tools also include anti-phishing capabilities that protect users from fraudulent schemes from compromised accounts.
- Bot Mitigation Solutions
- Bots pose a significant threat to e-commerce websites (e.g., account takeover attempts, credential stuffing, brute force attacks, inventory scalping, content scraping, DDoS attacks, etc. ), so use a tool to detect and block malicious bot activity.
- Most bot mitigation solutions use a combination of the following techniques to stop malicious bots:
- Rate limiting.
- CAPTCHA challenges.
- Behavior analysis (mouse movements, session duration, browsing behavior, etc. ).
- Device fingerprinting.
- Depending on where you operate, compliance requirements may mandate the use of bot mitigation measures.
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) protects a web application from attacks and unauthorized access. These firewalls sit between the server and the internet, where they perform the following tasks:
Analyze incoming and outgoing web traffic.
Inspect requests.
- Enforce security rules.
- Block malicious traffic.
- Here’s why WAFs are vital for e-commerce websites:
- WAFs block malicious users and prevent unauthorized access attempts.
These firewalls effectively prevent various eCommerce security threats, including SQL injections, XSS attacks, and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
WAFs provide granular inspection capabilities for HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
Most WAFs offer DDoS protection capabilities that detect and mitigate attacks by rate-limiting suspicious traffic.
- A WAF helps fulfill PCI DSS compliance requirements.
- These firewalls provide real-time monitoring and logging capabilities, so they detect and respond quickly to suspicious activity.
- WAFs have specialized rule sets and signatures tailored explicitly for web security, so they recognize attack patterns associated with most web-based threats.
- eCommerce Security Best Practices
Here are some further tips on how to keep eCommerce security threats at bay and make your e-retail website even safer:
- Regularly update your CMS, plugins, and extensions with the latest patches and bug fixes.
- Perform regular data backups of all databases with customer data (financial and PII).
- Periodically vet and review the security of integrated third-party apps, plugins, and services.
- Remove obsolete integrations or those that are no longer in use to minimize your attack surface.
- Perform periodic security audits, vulnerability scans, and penetration tests to identify and address weaknesses proactively.
- Use encryption at rest to protect stored customer data.
- Train all employees about eCommerce security threats and best practices.
Deploy an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) to boost network security and improve chances of detecting malicious activity.
Expunge former employees’ details and revoke their access once they leave the company.
- Boost email security and endpoint security at your company.
- Prepare an incident response plan that ensures the security team reacts optimally to threats.
- Use newsletters to educate customers about common security risks.
- You should also keep up with the latest cybersecurity trends and ensure all protection strategies align with the most recent cybercrime tactics.
- Improving eCommerce Security Belongs at the Top of Your To-Do List
- The eCommerce industry is a go-to target for cybercrime, so operating in this sector without a well-rounded security strategy is a recipe for disaster. Use this article to learn about the most significant eCommerce security threats and implement proper precautions to ensure you’re no easy target for cybercriminals.
