It involves manipulating human psychology and behavior to deceive people into divulging sensitive information or granting unauthorized access to networks, systems, and physical locations. It involves manipulating human psychology and behavior to deceive people into divulging sensitive information or granting unauthorized access to networks, systems, and physical locations.
Social engineering relies on exploiting powerful and near-universal emotions such as greed or fear instead of relying on technical hacking. It has even become the preferred tactic among hackers and its impact on cybersecurity cannot be overstated.
This article lists the 15 most famous cyber attacks where social engineering was the predominant factor. By understanding the hackers’ tactics, you will be able to identify and thwart social engineering attacks on you and your organization.
Social Engineering Examples
Let’s look at some of the most infamous social engineering cyber attacks in history.
1. Kevin Mitnick: Early Career
In the year 1994, Kevin Mitnick convinced Motorola, Novell and Nokia technical support staff to give him access to information he needed for troubleshooting. Mitnick used a combination charm, technical jargon and urgency to convince the support staff that he urgently needed the information. Mitnick was arrested, but he later said that he saw his actions as “simple crimes.” He further explained that his motivation was only to learn how phone networks operated.
Later in life, Kevin Mitnick, who
, used his talents for ethical hacking, becoming a respected security consultant and author.
2. Spear Phishing Attack on the Democratic National Committeepassed away in July 2023During the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign, a cyber attack targeted high-ranking officials and employees within the Democratic National Committee (DNC), the governing body of the Democratic Party in the United States.
The attackers crafted personalized and convincing phishing emails, a technique called spear phishing. When a victim clicked on malicious links, or downloaded malware-infected files, they unwittingly gave their login credentials to the attackers or allowed malware into their system. This breach led to the leak of sensitive emails during the 2016 U.S. Presidential campaign. It had major political repercussions, and raised concerns about foreign influence. Multiple cybersecurity firms conducted investigations that blamed the two Russian hacking groups, “Fancy Bear” (also known as “Cozy Bear”) and “Fancy Bear”, for the breach.
The DNC then contacted CrowdStrike to provide coordinated remediation services and disaster recovery. As a matter of concern,
reported that two Russian state-sponsored hackers had already infiltrated DNC’s networks as early as 2015.
3. Bangladesh Bank Heist
Contrary to the belief that bank robberies only happen in Western films, the Bangladesh Bank Heist was one of the most audacious and successful in history.their reportIn February 2016, hackers targeted the central bank of Bangladesh. They used insiders to send spear phishing emails with malware-infected files. When their targets eventually opened these attachments, they granted the hackers access to the bank’s network and systems.
Once inside, the attackers used internal processes and controls to manipulate the bank’s SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) system, a messaging network used by financial institutions to send and
.
Using fraudulent SWIFT transactions, the hackers attempted to transfer nearly $1 billion from the Bangladesh Bank to their accounts in the Philippines. The hackers managed to move approximately $1 billion despite some transactions being blocked or reversed. Sony Pictures Hack
In the year 2014, a group called “Guardians of Peace”, or GOP, targeted Sony Pictures Entertainment by sending spear-phishing emails that appeared to be official communications. GOP tricked Sony staff into revealing their login credentials, or clicking malicious links, which allowed them to gain access to the systems of the company. They remained undetected in the system for two months during which time they installed a listening device, a backdoor, a proxy, a destructive hard drive tool and a cleaning tool. Subsequently, they exfiltrated vast amounts of sensitive data, including unreleased movies, confidential business documents, employee records, and private email conversations.receive payments securelyOne of the most significant aspects of the data breach was the theft of several films, including
Annie$81 million,
Fury
, and
The Interview
. The films were released online before the official release date, which caused the studio to suffer a great deal of financial loss. The emails included candid opinions on celebrities, actors and business partners. While the identities of those behind GOP remain unknown, the United States Government pointed towards
. The attack was said to be motivated by the release The interview a comedy that revolves around a fictional plot against North Korean leader Kim Jong Un.5. Twitter Bitcoin ScamIn the summer of 2020, hackers attacked several high-profile Twitter profiles, including those belonging to Elon Musk and Barack Obama. They also targeted accounts belonging to Joe Biden, Kanye west, Bill Gates and .The attack began with LinkedIn scraping, which allowed them identify Twitter employees who had administrator privileges. Using paid tools available to job recruiters, they accessed these employees’ private contact information, including cell phone numbers.
Having selected their targets, they initiated contact by impersonating Twitter employees. The attackers used a remote work policy that was in place during the COVID-19 epidemic. Once they had breached the network the attackers sent out fake tweets to trick followers into thinking that they would get double the amount of Bitcoin if they send it to a specified address. The scam was a big hit. Many people sent Bitcoins to the addresses specified, and lost hundreds of thousands. NotPetya
Ransomware is a program designed to extort money, and ranges from basic lock screens to intricate code with encryption and data exfiltration capabilities.North Korea as the likely culpritEmerging in 2016, Petya is a ransomware strain that diverged from tradition by targeting the Master Boot Record (MBR) or the hard drive’s partition table, rendering the entire system inoperable. Petya initially distributed its payload as a PDF, spread through email attachments, spear phishing emails, and compromised websites. Kaspersky reported that more than 80 companies were affected, with the majority of infections occurring in Ukraine. Germany, on the other hand, was only 9%. The U.S. government estimates that the total damage caused by this attack exceeds .Experts believed this was a politically motivated and state-sponsored attack against Ukraine, as it primarily targeted the National Bank of Ukraine and coincided with the eve of the Ukrainian Constitution Day holiday.
7. Target Data Breach
The Target Data breach was the largest in history. It resulted in over 40 million credit card numbers, phone numbers, and addresses being compromised. The attackers compromised Target’s network through a third party vendor, Fazio Mechanical, a refrigeration contractor. In 2022, supply chain attacks will outnumber malware-based attacks. Hackers used the compromised vendor as a staging area to exploit an undiscovered vulnerability, gain a point-of-presence, escalate their privileges and attack Target’s systems. However, Fazio most likely relied on a free anti-malware solution that lacked real-time protection.many others8. Anthem Data Breach
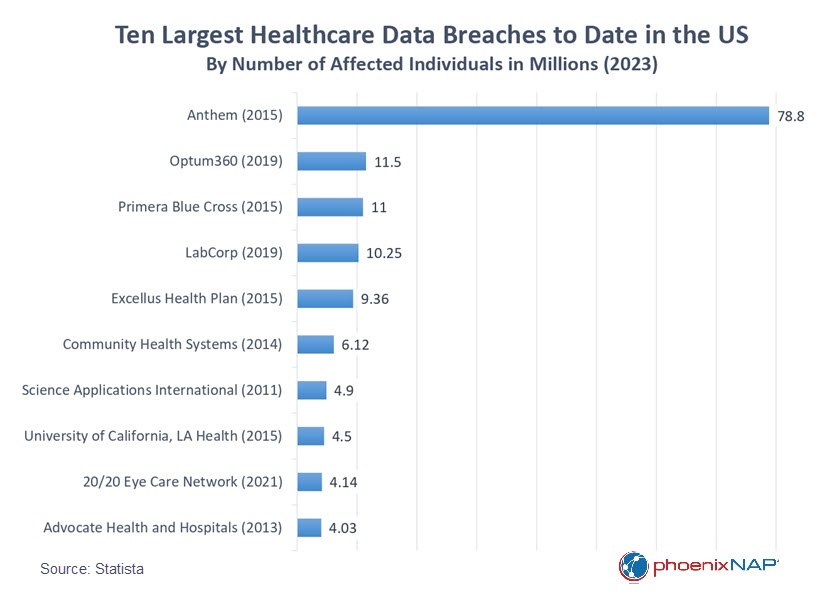
The Anthem data breach of 2015 was one of the most expensive and impactful phishing attacks in history.
Targeting one of the largest health insurers in the United States, the Anthem breach is the most extensive healthcare data breach ever recorded, giving the attackers access to the personal and medical information of
people. Anthem spent $230 million on remediation after the attack. Anthem had to spend $115 million on lawsuit settlements, $39.5 for the state attorney general’s investigation and $16 million more to cover the HIPAA audit fine and HIPAA violation fine. Evaldas Rimasauskas, Wire Fraud
From 2013, to 2015, Evaldas Rimasauskas created fake invoices that he used to steal $99 million and $23 from Google. With meticulously crafted emails, he deceived the companies’ employees into paying for goods they did not order or receive.
Using a technique similar to “typo squatting” or “URL hijacking,” Evaldas created a company in Latvia with a name closely resembling Quanta Computer Inc., a reputable Taiwanese electronics manufacturer. He used this disguise to conduct fraudulent multimillion dollar transactions with Google, Facebook and forward the funds into his accounts in Latvia, Cyprus and Cyprus. Surprisingly, neither company scrutinized the legitimacy of these documents.
His fraudulent activities ended when Lithuanian authorities apprehended him in 2017 and he was subsequently extradited to the United States. Rimasauskas was sentenced to a 60-month prison term after pleading guilty to one count
of wire fraud. AI Deepfake Scam Hits UK Energy Firm
In 2019, criminals used AI voice emulation software to steal EUR220,000 from a UK energy firm in a textbook example of a whaling attack – a spear phishing attack against a high-level executive.$10 billionThe scammers successfully impersonated the German CEO of the UK energy firm’s parent company. The scammers persuaded the UK CEO to urgently send money to a Hungarian supplier, which was, in fact, their account.
Shortly after the UK CEO sent the EUR220,000, the hackers called again, claiming they had sent money to reimburse him for the urgent transaction. The scammers called again the next day to request a second payment, this time impersonating the UK CEO. Consequently, he decided not to proceed with the second payment.

Following the transfer to the Hungarian bank account, the funds were moved to Mexico and distributed to other locations.
During the investigation, it was concluded that the perpetrators had employed commercial software to impersonate the German executive’s voice. This is one of the first known occurrences of AI voice mimicry being used for fraud.$18.5 million settlementTo date, investigators have not identified any suspects and have had to end the investigation.
The widespread digitalization of most aspects of society defines our era. Cybercrime is on the rise and cybersecurity will become more important as it grows. Read our article featuring seventeen security professionals on how to avoid social engineering attacks. Google Drive Scam
In the year 2020, a phishing scheme used push notifications to lure its victims to malicious websites. Scammers exploited a Google Drive flaw to send phony push notifications and emails, causing Gmail users click the “Open in Docs button” in the email. Upon doing so, users were directed to an authentic Google-hosted page, where they were asked to grant permission to a seemingly legitimate service called “Google Docs” to access their email account data.40%Unfortunately, providing permission granted the scammers access to the victim’s email account, contacts, and online documents. The malware sent an email to all the contacts on the victim’s list in order to spread the virus. Since the messages appeared legitimate, users were caught off-guard.
Upon receiving victim reports, Google promptly removed the documents utilized in the scam and addressed the security flaw.
12. Reveton
In the year 2012, Reveton was known as
. RaaS allows anyone to create highly effective malware campaigns. Reveton’s aggressive and intimidating nature is another notable feature. Nicknamed a “Police Trojan,” it locked the victim’s screen, displaying a fake message from law enforcement agencies, falsely accusing them of illegal activities such as copyright infringement or having a connection to child pornography.
To unlock the computer, the hackers demanded payment of a “fine,” exploiting official logos and language to instill urgency and fear in the victim. In this aspect, Reveton serves as a prime example of hackers skillfully using social engineering to establish credibility.nearly 79 millionMoreover, the ransomware utilized the user’s computer IP address and webcam imagery to create the illusion of constant monitoring and recording, manipulating the victim into succumbing to the ransom demand.
13. The Lapsus$ hacking group
In 2022, UK police arrested Arion Kurtaj, 18, and an unknown 17-year old for their involvement in hacking multiple organizations. The long list of companies includes Nvidia, Rockstar Games, Revolut, BT Group, Uber, and even the
.
The prosecutor assigned to the case emphasized that the hackers were not merely indulging in “juvenile pranks” but in sophisticated crime with the aim to profit.
The young hacker’s resume includes the following:
Stealing sensitive code and videos of Rockstar’s latest Grand Theft Auto game and leaking the information while demanding a ransom. Kurtaj allegedly used social engineering to pose as a contractor within the company and breach the firewall.
The pair accessed software building blocks for Nvidia’s products, publicly releasing some of the stolen data and threatening to release the rest if they didn’t receive a ransom. guiltyThe teenagers also allegedly hacked BT and engaged in SIM swap fraud, draining the cryptocurrency and bank accounts of multiple customers.
While being astonishingly competent for someone so young, the pair’s had a penchant for bragging that eventually led to their demise. After boasting about their exploits online, the police quickly
, who are still awaiting final sentencing.
14. Barbara Corcoran phishing incident
In the year 2020, Barbara Corcoran was almost scammed out of her money by a scammer who sent an email pretending to be from Corcoran’s assistant. The email instructed the bookkeeper that money should be wired to a fictional contractor who was working on a European Renovation Project.
Corcoran said, “The story seemed plausible since I do a great deal of real estate investing and renovations as a profession.” The bookkeeper’s German bank, which she used to send the money, froze it before the money reached the scammer in China. Corcoran explained her New York bank requested that the German bank suspend the transfer to allow her to present evidence of fraud.
15. Cabarrus County Hack
In 2018, hackers successfully persuaded Cabarrus County, NC officials to give them more than $2.5 million.
Posing as representatives from a construction contractor, the scammers contacted officials, pretending to be involved in the construction of a local high school, which was genuinely being built. The scammers were able to convince officials to switch the account where they paid for the construction of a school. To strengthen their deception, they provided what appeared to be legitimate documentation and approvals.

Once the criminals received the deposit, the funds were rerouted through various other accounts. Several weeks later, the scheme came to light when the genuine vendor contacted the officials, inquiring about a missed payment.
The authorities eventually recovered a portion of the funds, reducing the damage to
.
Conclusion
The first line of defense against cybercrime is having a strong password and following email security best practices. In many of the above examples, following these simple procedures could have been the difference between being hacked and not. AI-assisted firewalls and intrusion detection systems are at the forefront of modern cybersecurity threats. They can analyze vast amounts of data, detecting anomalies, patterns, and breaches in real time.
However, as formidable as these technologies are, they cannot single-handedly shield us from determined criminals. Prioritizing cybersecurity education for employees helps organizations create a human firewall to fortify their defenses. This also creates a united front against cyber threats.
