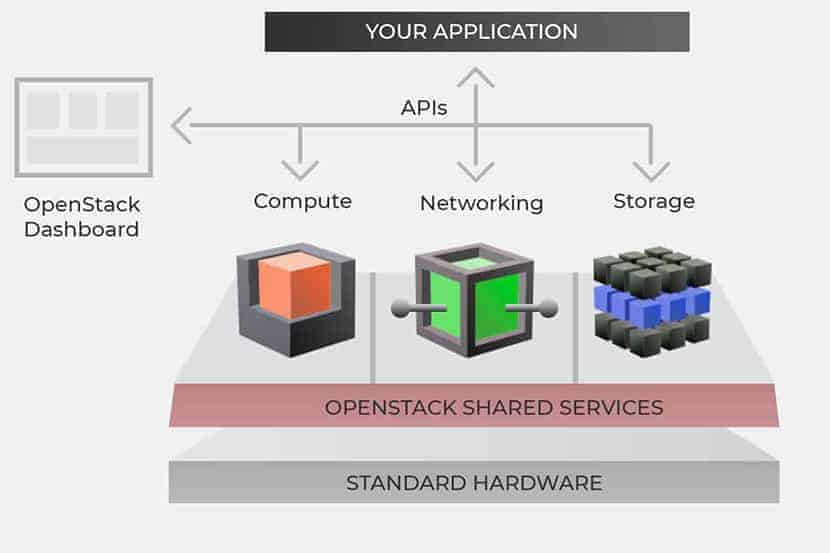
Cloud integration continues to evolve along with its platforms. Kubernetes, OpenStack and other cloud platforms are no longer just direct competitors. They can be combined in order to create cloud native applications. Kubernetes, the most popular container orchestration tool for managing/orchestrating Linux containers, is used by millions of people. It schedules, deploys and maintains applications. OpenStack lets businesses run their Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and is a powerful software application.
Kubernetes and OpenStack have been regarded as competitors, but in actuality, both these open-source technologies can be combined and are complementary to one other. Both offer solutions for problems that are similar, but on different layers. When you combine Kubernetes and OpenStack, it can give you noticeably enhanced scalability and automation.
It’s now possible for Kubernetes to deploy and manage applications on an OpenStack cloud infrastructure. OpenStack, as a cloud-orchestration tool, allows you to run Kubernetes Clusters more efficiently on white label hardware. Containers can be aligned with this open infrastructure, which enables them to share computer resources in rich environments, such as networking and storage.
Difference between OpenStack and Kubernetes
Kubernetes and OpenStack still do compete for users, despite their overlapping features. Both have their own set of benefits and use cases. It’s why it’s necessary to take a closer look at both options to determine their differences and find out which technology or combination is best for your business.
To present a more precise comparison between the two technologies, let’s start with the basics.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source cloud platform for managing containerized workloads and services. Kubernetes, a tool for managing clusters of containerized apps, is used by many. In computing, this process is often referred to as orchestration.
The analogy with a music orchestra is, in many ways, fitting. Kubernetes is similar to a conductor in that it coordinates microservices into a single application. It continuously monitors and adjusts its components. Kubernetes provides a combination of portability and extensibility with functionality. It facilitates declarative configuration as well as automation. Kubernetes manages workloads by using compute cluster nodes. Kubernetes also actively manages workloads, ensuring that their state matches with the intentions and desired state set by the user.
Kubernetes is designed to make all its components swappable and thus have modular designs. It can be used with public clouds, private clouds, or any combination. Kubernetes is popular among developers because it’s lightweight, accessible, and simple. It uses a simple model. Its service then works to align the two states and achieve and maintain the desired state. Its service then works to align the two states and achieve and maintain the desired state.
How is Kubernetes Employed?
Kubernetes is arguably one of the most popular tools employed when it comes to getting the most value out of containers. Its features ensure that it is a near-perfect tool designed to automate scaling, deployment, and operating containerized applications.
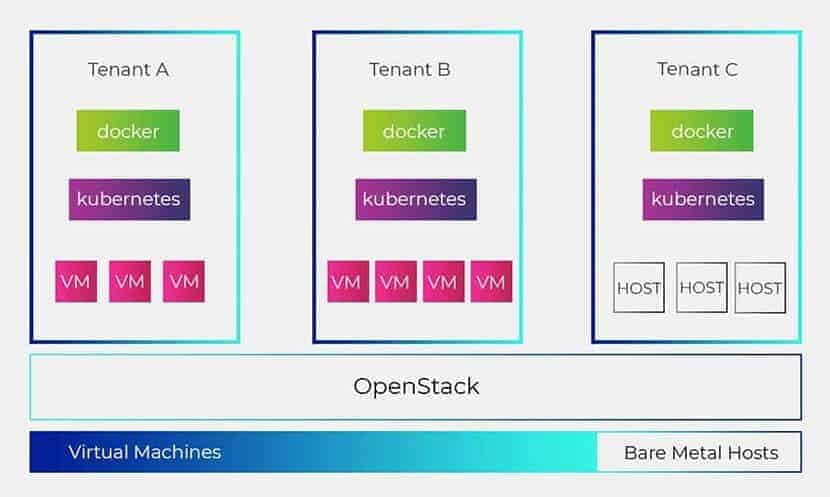
Kubernetes is not only an orchestration system. It is an interconnected set of control processes that are independent. Kubernetes is ideal for service consumers, such as developers working in enterprise environments. It provides support for programmable, agile and rapidly deployable environments. Kubernetes is ideal for service consumers, such as developers working in enterprise environments as it provides support for programmable, agile, and rapidly deployable environments.
- Kubernetes is used for several different reasons:High Availability:
- Kubernetes includes several high-availability features such as multi-master and cluster federation. Cluster federation allows clusters be linked. This setup exists so that containers can automatically move to another cluster if one fails or goes down.Heterogeneous Clusters:
- Kubernetes can run on heterogeneous clusters allowing users to build clusters from a mix of virtual machines (VMs) running the cloud, according to user requirements.Persistent Storage:
- Kubernetes has extended support for persistent storage, which is connected to stateless application containers.Built-in Service Discovery and Auto-Scaling
- : Kubernetes supports service discovery, out of the box, by using environment variables and DNS. For increased resource utilization, users can also configure CPU based auto-scaling for containers.Resource Bin Packing:
- Users can declare the maximum and minimum compute resources for both CPU and memory when dealing with containers. It slots the containers into wherever they fit, which increases compute efficiency, which results in lower costs.Container Deployments and Rollout Controls:
The Deployment feature allows users to describe their containers and specify the required quantity. It also manages deploying new changes. This enables users to pause, resume, and rollback changes as per requirements.
What is OpenStack?
OpenStack an open-source cloud operating system that is employed to develop public and private cloud environments. It is a cloud operating system that consists of interdependent microservices. This layer provides an IaaS for virtual machines and apps. OpenStack, first developed as a cloud infrastructure in July 2010, was a product of the joint effort of many companies, including NASA and Rackspace.
Their goal since has been to provide an open alternative to the top cloud providers. It is also a cloud-based operating system, which can manage large pools of computing, storage and networking resources via a central datacenter. OpenStack is gaining popularity because it offers open-source software to businesses who want to deploy their own private cloud infrastructure instead of using a public cloud platform. OpenStack is a complex system that consists of sixty components called services. Six of these core components control the most important aspects of a cloud. The services include compute, identity management, storage management, networking, and access management. Projects are responsible for relaying the tasks that create cloud environment. OpenStack does not virtualize resources itself; instead, it uses them to build clouds.
When it comes to cloud infrastructure management, OpenStack can be employed for the following.
OpenStack Containers
OpenStack provides a stable foundation for public and private clouds. Containers can be used to accelerate application delivery while simplifying management and deployment. Containers running on OpenStack can thus scale container benefits ranging from single teams to even enterprise-wide interdepartmental operations.
Network Functions Virtualization
OpenStack can be used for network functions virtualization, and many global communications service providers include it on their agenda. OpenStack separates a network’s key functions to distribute it among different environments.
Private Clouds
Private cloud distributions tend to run on OpenStack better than other DIY approaches due to the easy installation and management facilities provided by OpenStack. Its vendor-neutral interface is the most attractive feature. Its open API erases the worries of single-vendor lock-in for businesses and offers maximum flexibility in the cloud.
Public Clouds
OpenStack is considered as one of the leading open-source options when it comes to creating public cloud environments. OpenStack is able to create public clouds that offer services on par with other major cloud providers. This makes them useful for small scale startups as well as multibillion-dollar enterprises.
What are the Differences between Kubernetes and OpenStack?
Both OpenStack and Kubernetes provide solutions for cloud computing and networking in very different ways. Some of the notable differences between the two are explained in the table below.
Points of Difference
Kubernetes
| OpenStack | Classification | Classified as a Container tool |
| Classified as an Open Source Cloud tool | User Base | It has a large Github community of over 55k users as well as, 19.1 Github forks. |
| Not much of an organized community behind it | Companies that Use them | Google, Slack, Shopify, Digital Ocean, 9GAG, Asana, etc. |
| PayPal, Hubspot, Wikipedia, Hazeorid, Survey Monkey, etc. | Main Functions | Efficient docker container and management solution |
| A flexible and versatile tool for managing Public and Private Clouds | Tools that can be Integrated | Docker, Ansible, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine, Kong, Etc. |
| Fastly, Stack Storm, Spinnaker, Distelli, Morpheus Etc. | How Can Kubernetes and OpenStack Work Together? | Can Kubernetes and OpenStack work together? It is a question that many potential users ask. Kubernetes and OpenStack together can simplify management of OpenStack components for enterprises. In this way, users benefit from a consistent platform for managing workloads. |
Kubernetes and OpenStack can be used together to reap the combined benefits of both the tools. Kubernetes can benefit from a more robust framework to deploy and manage applications by integrating Kubernetes with OpenStack. Kubernetes’s features, scalability, and flexibility make ‘Stackanetes’ an efficient solution for managing OpenStack and makes operating OpenStack as easy as running any application on Kubernetes.
Benefits of Leveraging Both OpenStack and Kubernetes
Faster Development of Apps
Running Kubernetes and OpenStack together can offer on-demand and access-anytime services. It also helps to increase application portability and reduces development time.
Improving OpenStack’s lifecycle management
Kubernetes, along with cloud-native patterns, improve OpenStack lifecycle management through rolling updates and versioning.
Increased Security
Security has always been a critical concern in container technology. OpenStack provides a high-level of security to solve this problem. It supports the verification of trusted container content by integrating tools for image signing, certification, and scanning.
Standardization
By combining Kubernetes and OpenStack, container technology can become more universally applicable. This makes it easier for organizations to set up as well as deploy container technology, using the existing OpenStack infrastructure.
Easier to Manage
OpenStack can be complex to use and has a steep learning curve, which creates a hindrance for any users. The Stackanetes initiative circumvents the complexity by using Kubernetes cluster orchestration to deploy and manage OpenStack.
Speedy Evolution
Both are widely employed by tech industry giants, notwithstanding Amazon, Google, and eBay. The popularity of the software drives it to innovate and develop faster. They accelerate the evolution of software to provide solutions as soon as issues arise. Evolving and simultaneously integrating, creates rapidly upgraded enterprise-grade infrastructure and application platforms.
Stability
OpenStack on its own lacks the stability to run smoothly. Kubernetes uses a large scale distributed system that allows it to run smoothly. By combining the two, OpenStack can use a more modernized architecture, which also increases its stability.
Kubernetes and OpenStack are Better Together
There has always been competition between OpenStack and Kubernetes, both of whom are giants in the open-source technology landscape. It’s no surprise that some users are surprised when we discuss the benefits of using both tools in conjunction. Combining the two tools is the best solution to achieve scalability, automation and scalability. DevOps would be more free to build cloud-native apps if they combined their efforts. Both Kubernetes and OpenStack have their advantages and use cases. making it very difficult to compare between the two, as both of them are used in different contexts.
OpenStack, together with Kubernetes, can increase the resilience and scale of its control panel, allowing faster delivery of infrastructure innovation. Both will continue to innovate at a rapid pace thanks to these complementary yet different technologies.