This number is expected skyrocket up to. IDC estimates that by 2022, these devices will generate 73.1 gigabytes of global data, which is 300% more than the current year 2019. This data must be sorted and analyzed quickly and efficiently to ensure a better user experience for applications and improve business decisions. Edge computing is the technology making this happen. 30.9 billion by 2025 However, deploying modern workloads such as microservices, machine learning apps, and AI close to the edge brings a number of challenges an organization’s infrastructure needs to address. To benefit from edge computing, businesses need to find a perfect balance between their IT infrastructure and their end-user needs.
Challenges of Edge Computing
To perform optimally, edge workloads require the following:
Proximity
– Storage and compute resources need to be close to the data source.
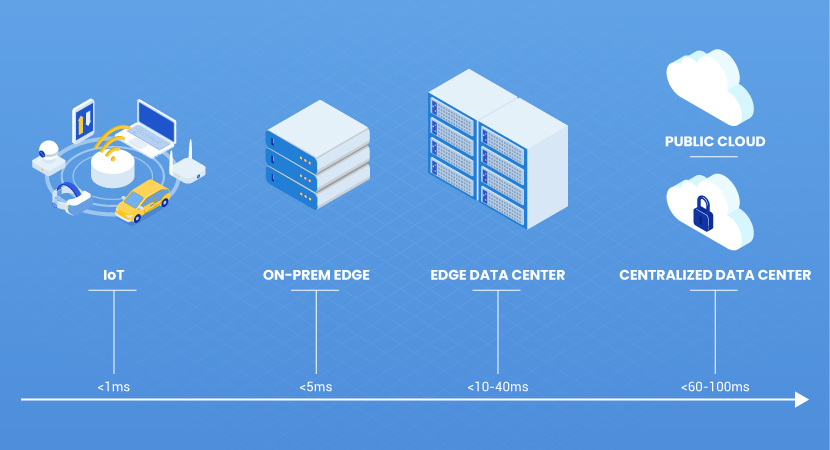
- Responsiveness – Apps need data transfer latencies to go from under 5 to 20 milliseconds.
- Mobility – Many edge devices move and compute and storage resources need to follow.
- The data transfer latency of remote and centralized public cloud computing model does not cater to the needs of modern edge workloads. On the other hand, building a decentralized network to support edge workloads comes with an intimidating list of its own challenges.Logistics Complexities
Managing disparate edge compute, network, and storage systems is complex and requires having experienced IT staff available at multiple geographical locations at the same time. This takes time and puts a significant financial strain on organizations, especially when running hundreds of container clusters, with different microservices served from different edge locations at different times.
Bandwidth Bottlenecks
According to a report by Morgan Stanley, radars, sensors, and cameras of autonomous vehicles alone are expected to generate.
To make life-saving decisions fast, the data these four-wheeled supercomputers create needs to be transferred and analyzed within fractions of a second.
Similarly, numerous edge devices collect and process data simultaneously. Sending such raw data to the cloud can compromise security and is often inefficient and cost-prohibitive.up to 40 TB of data an hourTo optimize bandwidth costs, organizations typically allocate higher bandwidth to data centers and lower to the endpoints. As a result, the uplink speed becomes a bottleneck as applications push data from the cloud out to the edge. At the same time, edge data is also being sent back in the opposite direction. As the edge infrastructure grows, IoT traffic increases and insufficient bandwidth causes massive latency.
Limited Capability and Scaling Complexities
The smaller form factor of edge devices typically leads to a lack of power and compute resources necessary for advanced analytics or data-intensive workloads.
Also, the remote and heterogenous nature of edge computing makes physical infrastructure scaling a major challenge. Scaling the infrastructure at the edge is not limited to adding hardware. If not planned and executed correctly, horizontal scaling can lead to increased costs due to overprovisioning, or suboptimal application performance due insufficient resources. If not planned and executed correctly, such horizontal scaling can lead to increased costs due to overprovisioning, or suboptimal application performance due to insufficient resources.
Data Security
As computing moves to the edge, infrastructure goes beyond the multiple physical and virtual layers of network security offered by centralized computing models. If not adequately protected, the edge becomes a target for various cyber threats.
Malicious actors can inject unauthorized code or even replicate entire nodes, stealing data and tampering with it while flying under the radar. The malicious actors can also affect data transfer across the network through routing information attacks that impact throughput, latency and data paths by deleting and replacing data. DDoS attacks are another common threat to data security at the edge. They aim to overwhelm nodes in order for them not only to drain batteries but also to exhaust their communication, computation and storage resources. Only the most important data from IoT devices should be analyzed. Without secure and compliant long-term data retention and archival solutions, this often leads to excessive data accumulation and data sprawl at the edge, further increasing vulnerability.
Data Access Control
The fact that edge devices are physically isolated means that, in this distributed computing system, data is handled by different devices, which increases security risks and makes data access difficult to monitor, authenticate and authorize.
Privacy of an end-user or end device is another critical aspect to maintain. To ensure that every user is counted, multi-level policies must be implemented. Making this possible while meeting real-time data latency requirements is a major challenge, especially when building edge infrastructure from scratch.
Having a physically close, pre-configured solution built by an ecosystem of partners offering optimized hardware and infrastructure management tools mitigates edge computing challenges. Edge infrastructure can help reduce application response time and improve data delivery. By bringing compute, storage, and network resources closer to the source of the data, edge data centers offer various benefits to both organizations and their workloads.
These include:
Minimized latency due to physical proximity
– Improving data delivery and reducing application response time.
Enhanced security and privacy
– High levels of physical and cyber security on-prem, less data uploaded to the cloud, and reduced amount of vulnerable data in transit.
- Increased reliability – Redistributing workloads to smaller data centers takes the load off central servers increasing performance and data availability.
- Cost optimization – With managed services and pre-configured infrastructure solutions, edge data centers help organizations reduce TCO and cut IT costs.
- Through high-performance hardware and software technologies offered as a service, platforms like Bare Metal Cloud help businesses improve time to action and avoid data transfer bottlenecks. Edge workloads are benefited by automation-driven infrastructure provisioning.Konteynerli uygulamaların ve Mikro hizmetlerin desteği. Aynı zamanda, tek kiracılı, güvenli bir kaynağın yanı sıra merkezi izleme ve kontrol, tam altyapı kontrolüne olanak tanır. Son olarak, önceden yapılandırılmış sunuculardan yararlanmak, raf, güç, soğutma, güvenlik veya diğer altyapı bakım faktörlerine olan ihtiyacı ortadan kaldırarak şirket içi ekiplerin bunun yerine uygulama optimizasyonuna odaklanmasına olanak tanır. Çözüm
- Kablosuz iletişim teknolojileri, IoT cihazları ve uç bilgi işlem gelişmeye devam ediyor, birbirlerini yeni atılımlara çağırıyor ve üstesinden gelinmesi gereken yeni zorluklar yaratıyor.IoT ekosisteminde daha fazla veri üretilip dağıtıldıkça bilgi işlem, depolama ve ağ teknolojilerinin uyum sağlaması gerekiyor. Uç veri merkezleri gibi çözümler, BT satıcıları ve hizmet sağlayıcılar arasındaki ortaklıklar yoluyla yaratılır.Veri kaynağına yüksek performanslı, güvenli veri depolama ve analitiği getirerek kuruluşların uç bilgi işlem zorluklarının üstesinden gelmesine yardımcı olurlar.