Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS) is a cloud computing service that allows companies to use a database without setting up physical hardware. Users also do not need to install software or hire staff members to maintain the underlying technologies.
DBaaS simplifies database management with one-click operations, eliminates time-consuming tasks, and grants the agility for faster software development.
Read on to learn what DBaaS technology offers and how to select the ideal DBaaS provider for your team.
Database-as-a-Service Features
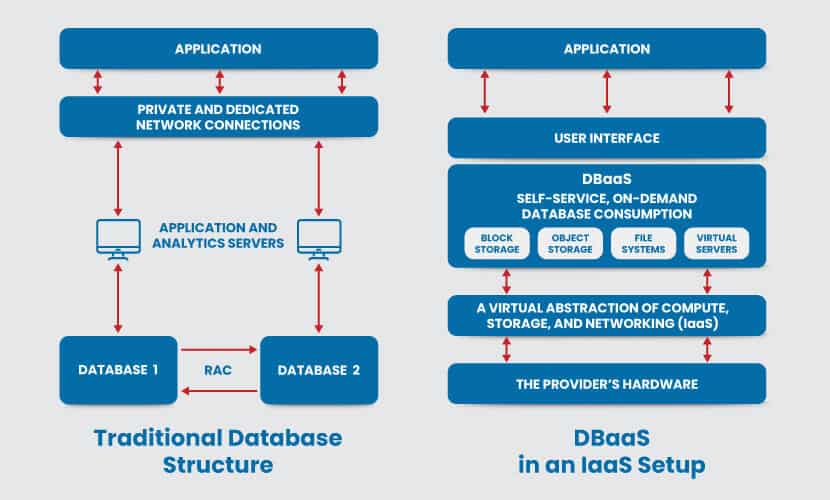
In a traditional setup, the database server is part of the on-premises computing infrastructure. Local staff are responsible for installing and managing the database, as well as protecting and scaling it. The service provider handles the high-level database administrative (DBA) tasks, including:
The DBaaS customer’s only responsibilities are using the database and controlling its content. However, if the company desires more control over the database, the DBaaS provider can enable more user involvement.
Another common name for DBaaS is the
managed database service. This type of cloud service covers both relational and non-relational databases. DBaaS eliminates the need to hire and train a team to manage the database. One staff member can control the database instances using an API and management dashboard. The dashboard allows one-click operations that simplify complex processes such as provisioning and specification.
Once the console receives instructions from the user, the DBaaS platform provisions the database and returns a query-able endpoint. The user can use this code directly in the application.
Database-as-a-Service enables users to operate a database with a common set of abstractions.
height=500 vs.structureprimitives) without knowing the implementations. The DBaaS model also provides simple mechanics for adding users.
- Creating schemas.
- Granting permissions.
- Activity tracking. The DBaaS model also provides simple mechanics for:
- Adding users.
Creating schemas.
Granting permissions.
- Activity tracking.
- Database-as-a-Service: Practical Applications
Database-as-a-Service has two primary consumers:
Organizations that manage and maintain the cloud
Teams that consume cloud resources (either traditional development or DevOps teams)
DBaaS is ideal for small to medium-sized companies without big IT departments. As DBaaS takes on the financial burden of hardware and maintenance, smaller teams can build apps that they cannot afford to support on-premises.
DBaaS is also a popular option for teams that want to set up and scale databases for complex distributed apps. For example, in an IaaS and DBaaS setup, the DBaaS solution can request resources from the IaaS platform, which automatically manages the provisioning, storage, and networking processes.
- Companies also use DBaaS platforms to support specific releases or restrict the configurations users can provision. A company may restrict its developers from provisioning SSDs and limit their access to traditional hard drives. Meanwhile, DevOps engineers can have the ability to provision higher-capacity servers with SSDs.
- Databases processing data with strict regulatory requirements are not suitable for DBaaS due to the risks of storing data in the cloud. Also, mission-critical applications that demand 99.999% uptime are a better fit for in-house infrastructures.
- Setting up DBaaS
- Amazon (Amazon Aurora, DynamoDB, Amazon RDS, and SimpleDB)
- Google Cloud (GC Bigtable, Google Cloud Datastore, GC Spanner, Google Cloud SQL)
- Microsoft Azure (Microsoft SQL Database, MA Table Storage, Microsoft DocumentDB)
- Compose (IBM)
IBM CloudantMongoDB Atlas Oracle Database Cloud Service
The cloud and database services do not need to be from the same provider. A team could, for example, set up Bare Metal Cloud to meet cloud needs and then pair it with Microsoft SQL Server. However, not all cloud platforms support all database management systems
(DBMS), so perform research before combining different providers.
DBaaS Benefits
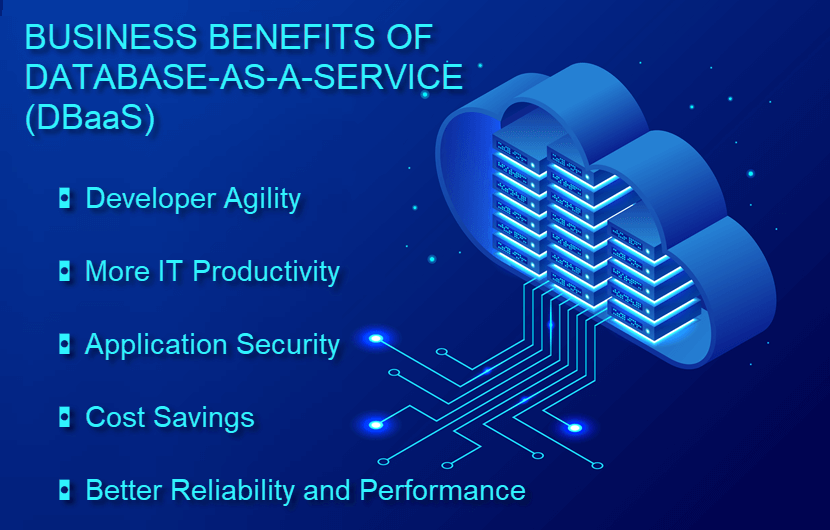
- DBaaS offers significant operational and financial advantages over standard on-premises databases.
- Developer Agility
- Standard database deployment is a complex, multi-step process that requires various tasks. A typical deployment looks like this:
- A developer opens a request in the ticketing system.
- The ticket stays in the queue until it reaches the top of priorities.
- The IT team evaluates the ticket.
If the request is valid, the team allocates the compute, storage, and networking resources for the new database.
Resource configuration and installation start.
The developer receives an entry point to the database and begins to use the new setup.
This process is far from agile, especially if the team is trying to transition to DevOps. Deploying databases this way is both prone to errors and time-consuming.
The DBaaS model requires zero IT intervention and automates the deployment process. After the company sets the standard for database provisioning, a developer will be able to handle the deployment. This self-service model allows companies to accelerate the software development cycle. The databases also become more consistent, which leads to better system reliability.
More IT Productivity
- Standard database management requires the team to handle the tuning, monitoring, patching, upgrading, and resizing of the database. As companies grow, the number and types of databases that require management increase, and these tasks become even more time-consuming.
- With DBaaS, the team saves valuable time as:
- The provider takes on most administrative duties.
Complex procedures (like deployments, upgrades, and configuration changes) happen automatically.
Developers can spin up and destroy multiple databases with a single operation.
The lack of repetitive duties and micro-managing allows the team to focus on more impactful tasks, such as building applications and innovating.
- Application Security
- Cloud database providers typically offer enterprise-level security. Good providers protect your databases with:
- Data encryption (both at rest and in transit).
- Integrated access management.
Controls for regulatory compliance standards.
End-to-end network security with micro-segmentation and virtual private networks.
The result of high-level security is less risk of data loss. Additionally, all major cloud providers offer a service-level agreement (SLA) that guarantees uptime.
Improve your data center security by adding strategic layers of protection that keep your data and systems safe.
- Cost Savings
- Database-as-a-Service is a cost-effective alternative to an in-house database setup. DBaaS lets a business pay a predictable fee based upon the resources consumed. A business saves money by not having to invest in:
- Expensive, power-hungry hardware.
- Data centers.
- Software licensing.
Additional on-hand capacity.
Skilled staff to manage and maintain the infrastructure.
Database-as-a-Service also prevents unnecessary resource overhead. Like any cloud offering, users control how many resources they consume, which allows a business to ensure optimal consumption at all times.
Better Reliability and Performance
DBaaS solutions have high availability and run at peak performance. In the case of failure, the platform reroutes traffic to a replica and maintains uptime.
Database-as-a-Service has excellent scalability. Users can easily and quickly add computing and storage capacity to meet processing demands. It is easy to scale down when not in peak usage. A DBaaS can monitor the database to detect spikes. If the user sets up policies for usage thresholds, the platform can automatically scale out as demand increases and scale back once demand reduces.
DBaaS Disadvantages
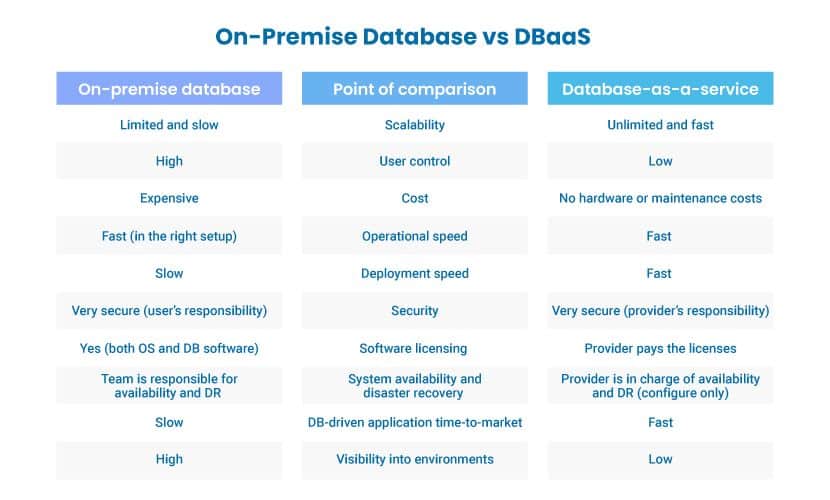
- Despite notable benefits, DBaaS also has several disadvantages when compared to an on-premises database setup. The disadvantages include:Lack control:
- In-house staff do not have access the storage or servers behind the database. If the user’s connection goes down or the provider experiences an outage, the customer cannot reach the stored content.Security concerns:
- Storing data on a cloud can lead to a breach if the provider is not careful. Also, the customer company does not influence the physical safety of servers.Latency problems:
Accessing data over the internet can lead to performance issues, especially when loading large amounts of data.
While worrying, these issues should not be a problem if the company partners with a reputable DBaaS provider.
Check out our article On-Premise vs Cloud to better understand how these terms relate and contrast.
How to Choose a DBaaS Provider?
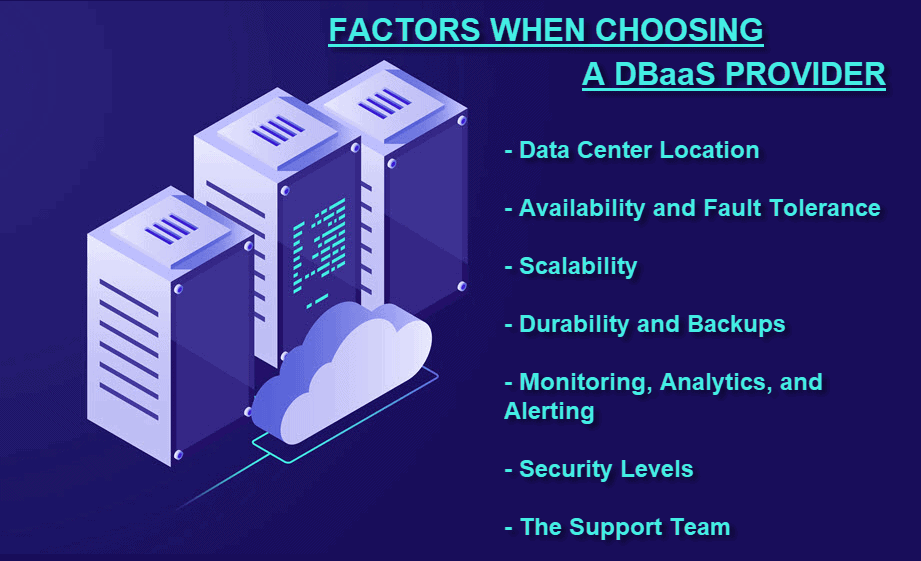
Finding the right DBaaS provider starts by determining which database technology is the right fit for your application’s technical needs. Consider the following factors to find the best DBaaS for your business. Too much distance between the infrastructure leads to two problems:
Latency:
- The time it takes to send a request to the database and receive a response impacts app performance.Security:
- The communication between your application and database needs to be private. Proximity with the database layer ensures the data is not traveling over the open internet.Ideally, your app server and database server should be in the same data center. The less space there is between the devices, the better.
Availability and Fault Tolerance
High availability is essential to your application. Consider the following factors when choosing your DBaaS provider:
Does the provider have an availability SLA? What is their uptime guarantee?
- How does the provider replace faulty components?
- How does the system failover work? Is the process automatic, or does the customer need to intervene?
- Does the provider offer fault tolerance via database clustering? If yes, what is the isolation between the nodes in the cluster?
- Does the provider have a global disaster recovery in the case of a regional outage?
- Scalability
Your DBaaS provider must provide a service that maintains optimal performance as your data volume grows. Do not rely on benchmark tests from the provider if your application requires high processing. If you anticipate a significant increase in data volume or traffic then ensure that the provider allows your team to easily scale the service. Two types of scaling are offered by providers:
If you have a large dataset in your app, it is better to use horizontal scaling. Vertical scaling is better suited for smaller workloads because of the limitations on the amount of hardware that can be fitted into a single device.
Check out our Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling comparison article to learn about two distinct strategies for adding more resources to an IT system
Durability and BackupsAll solid providers have a robust backup and recovery system in case of system failure and human error. Answer the following questions before you choose your DBaaS provider:Does the provider create data backups automatically?
What backup tools does the provider use?
Can customers make recurring plans to create backups on a custom schedule?
Can users easily and quickly restore their data?
- Does the DBaaS provider support the point-in-time restore capability?
- Monitoring, Analytics, and Alerting
- Monitoring, analytics, and alerting give insight into the health of your database. Monitoring and alerts must be enabled to inform customers when metrics are outside of the normal range. Consider the following when choosing your DBaaS provider:
- Can you create custom alerts?
- Are there automatic alerts in case of a component failure?
Will you have real-time insight into all performance metrics?
Does the provider offer historical reporting of database metrics?
- Is there easy access to database log files?
- Security Levels
- A DBaaS provider must ensure your data’s safety and provide you with tools to protect cloud assets from unauthorized access. Answer the following questions to find the right provider:
- Does the platform verify users before they access the cloud database? Is there support for
- ?
Does the provider log all access requests?
Does the platform support database communication via SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) with certificate validation?
- Is there support for data-at-rest and in-transit encryption?2FADoes the provider run penetration tests to ensure high levels of security?
- The Support Team
- A fast and helpful support team is vital for providing advice and responding to emergencies. The following questions will help you pick a provider with a solid support team:
- Does the provider charge an additional fee for support?
- Does the SLA include support response times?
Do you need to purchase premium support to guarantee quick response times?
What is the provider’s reputation when it comes to customer care and support?
- A Cost-Effective Alternative to On-Premises Database Management
- Database-as-a-Service can add agility and flexibility to development teams no matter the size or industry. Use DBaaS as a cost-effective alternative to on-premises database management.