To reduce the risks of exposure, we need a novel approach that helps us understand potential areas of attack, prioritize our actions effectively, and track progress over time. To decrease the risks of exposure, we need a novel approach that helps us understand potential areas of attack, prioritize our actions effectively, and track progress over time.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management goes beyond just managing vulnerabilities. It is a forward-thinking framework that focuses on managing a broader range of risks likely to impact our business priorities.
This article will outline an effective method for establishing a coherent and practical security improvement plan that business executives can easily comprehend, and engineers can effectively implement.
What is Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)?
In July 2022, Gartner introduced the concept of CTEM, a framework that enables organizations to evaluate the vulnerability of their physical and digital assets continually and consistently.
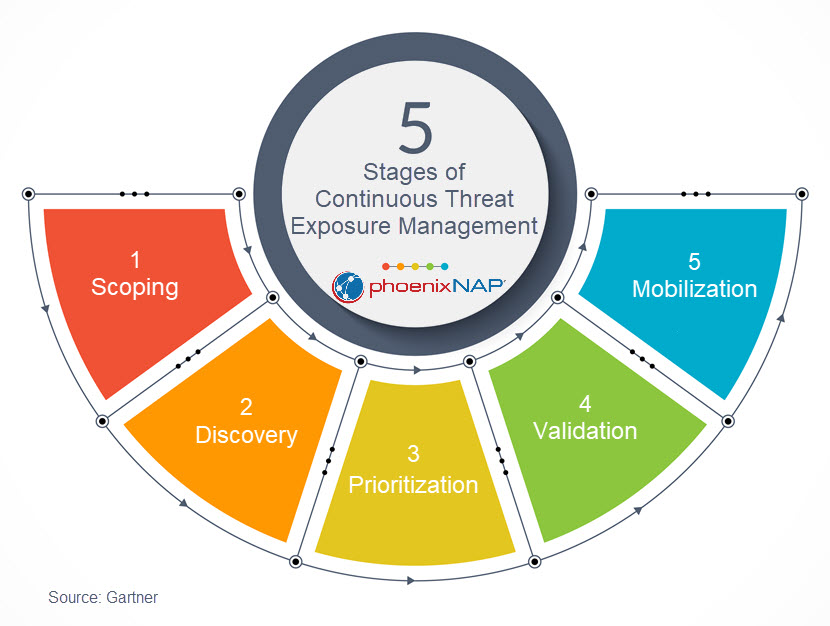
The objective of the CTEM program stages is to establish well-defined security and risk management strategies that align with business objectives. Organizations can improve their security posture by continuously minimizing risks, improving resilience and promoting collaborative efforts. Scoping
Every CTEM project begins with defining a specific scope that encompasses business-critical assets that need to be identified, tested, and strengthened.
Ideally, scoping should incorporate all stakeholders, including IT Operations, Governance, Risk, Compliance, and asset owners. They need to jointly consider the entire attack surface of the enterprise, both internal and external, including factors such as cloud infrastructure, software supply chain and application risks, as well as buildings and hardware.
Read our article on the difference between attack vectors and attack surfaces, two interconnected security concepts crucial for effective preparation against malicious activity.
2. Discovery
During this stage, security teams take inventory of assets and assess risk profiles based on the earlier scoping process. They map out assets, vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, technology, and risk to gain a comprehensive understanding.
However, not every vulnerability or misconfiguration is equally relevant. It is not practical to try and fix all vulnerabilities at once. Prioritizing vulnerabilities is therefore essential in order to identify which ones should be addressed first. Prioritization
The purpose of prioritization is to establish which threats are more likely to be exploited and pose an imminent risk to the enterprise. Prioritization is more than just assigning severity ratings to vulnerabilities. Security teams should consider the following factors to make informed decisions:
Exploitability: Assess how easy it is for an attacker to exploit the threat.
Effectiveness of Security Controls: Evaluate the mitigation capabilities of existing security measures.
Network Topology
: Understand how network security threats can spread through the organization’s infrastructure.
- Risk Appetite: Consider your organization’s risk tolerance, prioritizing threats that align with the risk threshold.
- Overall Impact: Evaluate the potential consequences of a threat, including financial losses, reputational damage, operational disruptions, and compliance violations resulting from successful exploitation.
- 4. Validation During the validation phase, organizations evaluate how they would handle an actual attack and assess their ability to defend against it. This evaluation must go beyond identifying potential threats and involve validating security controls and determining the order of vulnerability remediation using simulated attacks.
- By performing a combination of technical assessments, such as penetration testing, red teaming, data breach and attack simulation, and attack path analysis, Security Teams provide evidence that supports their prioritization decisions and effectively demonstrate the need for remediation to both IT Operations and business stakeholders. These findings are crucial in the process of establishing and improving a cybersecurity incident response plan.
- Information security management is one of the core components of an ironclad business continuity plan. Follow our 10-step checklist to improve your business continuity plan. Mobilization During the mobilization step, organizations take action to improve their security posture. They integrate the findings from the validation process into the steps needed to fix vulnerabilities, allowing for swift implementation and improved efficiency.
To prevent the accumulation of a long lists of unresolved vulnerabilities, it is crucial to address delays caused by approval processes and misunderstandings between different teams. Prioritizing threats that are aligned with business goals will help to address the most important ones quickly. This way, vulnerabilities are fixed before malicious actors can exploit them, threatening business continuity management efforts.
It’s crucial to involve all stakeholders, even if they are less familiar with security matters, to ensure a comprehensive approach.
How is CTEM Different from Traditional Vulnerability Management Programs?
CTEM distinguishes itself from conventional vulnerability management programs because of the following six characteristics:
1. Proactive Approach
While traditional programs reactively identify and patch known vulnerabilities, CTEM adopts a proactive stance by continuously monitoring the threat landscape. Prioritizing remediation of identified vulnerabilities and threats before hackers exploit them, CTEM prioritizes their remediation. CTEM has a broad scope. CTEM recognizes that threats can be posed by a variety of sources, including configuration errors, misused passwords, and insider threat. Business-Aligned Prioritization
Traditional vulnerability management often struggles to effectively prioritize remediation efforts, resulting in patching all vulnerabilities regardless of severity. CTEM, on the other hand, aligns its priority with business objectives by focusing on the most important threats and vulnerabilities which could have a negative impact on the organization’s most valued assets.
4. Continuous Improvement
Traditional programs typically adopt a point-in-time approach, conducting periodic scans and then moving on. CTEM, on the other hand, promotes a continuous cycle of improvement by constantly monitoring, evaluating and improving an organization’s security posture. Integration with Security Controls
Traditional vulnerability management often operates separately from other security measures. CTEM places a strong emphasis on validation. While traditional frameworks heavily rely on vulnerability assessments, CTEM places a significant focus to test the organization’s defenses against simulated attacks. Emphasis on Validation
While traditional frameworks heavily rely on vulnerability assessments, CTEM places significant emphasis on validation to test the organization’s defenses against simulated attacks.
Benefits of CTEM
According to Gartner, organizations that implement a continuous threat exposure management program will experience a
in the likelihood of suffering a breach by 2026.
By adopting the CTEM approach, organizations proactively and predictively address threats rather than rely on reactive and responsive measures. This strategy enables them to reduce vulnerability noise, minimize risks, and foster improved collaboration across distinct organizational functions.
However, to effectively implement CTEM, enterprises must ensure that their facilitating tools are not siloed and are fully integrated.
Challenges of CTEM Implementation
Implementing a CTEM program is a worthy initiative, but you must first address some challenges to ensure successful execution. By tackling these challenges now, you can save yourself time and frustration in the future. Aligning non-security teams with security teams
IT Infrastructure, DevOps and security often have communication gaps. It becomes more difficult to overcome this disconnect when implementing CTEM or other new programs. This can cause confusion over ownership, misalignment of expectations, and many other problems. It is not sufficient to give them a list of tasks. Ask for their input, understand their needs and identify how you can make work easier. Seek their input, understand their needs, and identify how you can make their work easier.
Additionally, consider starting a security awareness training program to educate employees about common types of cyber attacks and their business impact to help them understand how they are relevant to their work.
2. Create a comprehensive view
A CTEM program that is comprehensive will cover a wide range of areas such as software and cloud vulnerabilities, network security and other related issues. Each area has traditionally operated in a silo, with its own owners, tools and issues. CTEM aims to unite these areas so as to aggregate information in a way that enables everyone to understand priorities and responsibilities and create a holistic perspective.
To overcome this challenge, designate a “point person” who can take a high-level view and understand how all the covered areas converge and impact each other. This person doesn’t need to be an expert in every security or tool category. They should still be able to see the bigger picture, and make sure that professionals with specific knowledge are continually addressing all areas.

3. Managing Diagnostic Noise
With the many areas of CTEM and their tools and alerts there can be a lot of noise. CTEM’s primary goal is to streamline information. Nevertheless, this program can result in significant signal interference from multiple tools. Threefold decrease to address this challenge:
Accept that fixing every issue is nearly impossible and focus on prioritization and efficiency.
Identify scopes and exposures that attackers are most likely to exploit and that have the greatest business impact.
Consider starting with a “crawl, walk, run” approach, where you begin with a small scope and gradually expand as the program matures.
The average cost of a data breach hit a record high of $4.35 million in 2022, marking a 2.6% increase from the previous year and a 12.7% surge from 2020. Read my article to understand the factors that contribute to the costs and discover effective strategies for mitigating these losses.
Traditional approaches to ensuring security are straining to keep up with rapidly evolving threats and expanding attack surfaces. The results of technology-focused assessments are often lengthy reports with generic recommendations, which business executives seldom act on. Vulnerability management programs also struggle to keep pace with the growing number of liabilities within large organizations.
These challenges make traditional vulnerability mitigation methods less effective. The goal of CTEM is to provide a consistent and actionable plan for improving security that is easily understandable and cost-effective to implement.
The bottom line is that by leveraging CTEM, organizations can effectively enhance their security by identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.